Blockchain is a term you’ve probably heard floating around—especially if you’ve been paying attention to the world of cryptocurrency. But blockchain isn’t just about Bitcoin or other digital currencies. In fact, this revolutionary technology has the potential to change industries far beyond just finance. From healthcare and supply chains to voting systems and real estate, blockchain is starting to reshape the way we do business, communicate, and store data.
If you’ve ever found yourself a bit confused about what blockchain actually is, don’t worry! This guide will break it down into simple, easy-to-understand concepts, so you can get a better grasp of this powerful technology.
So, What Exactly is Blockchain?
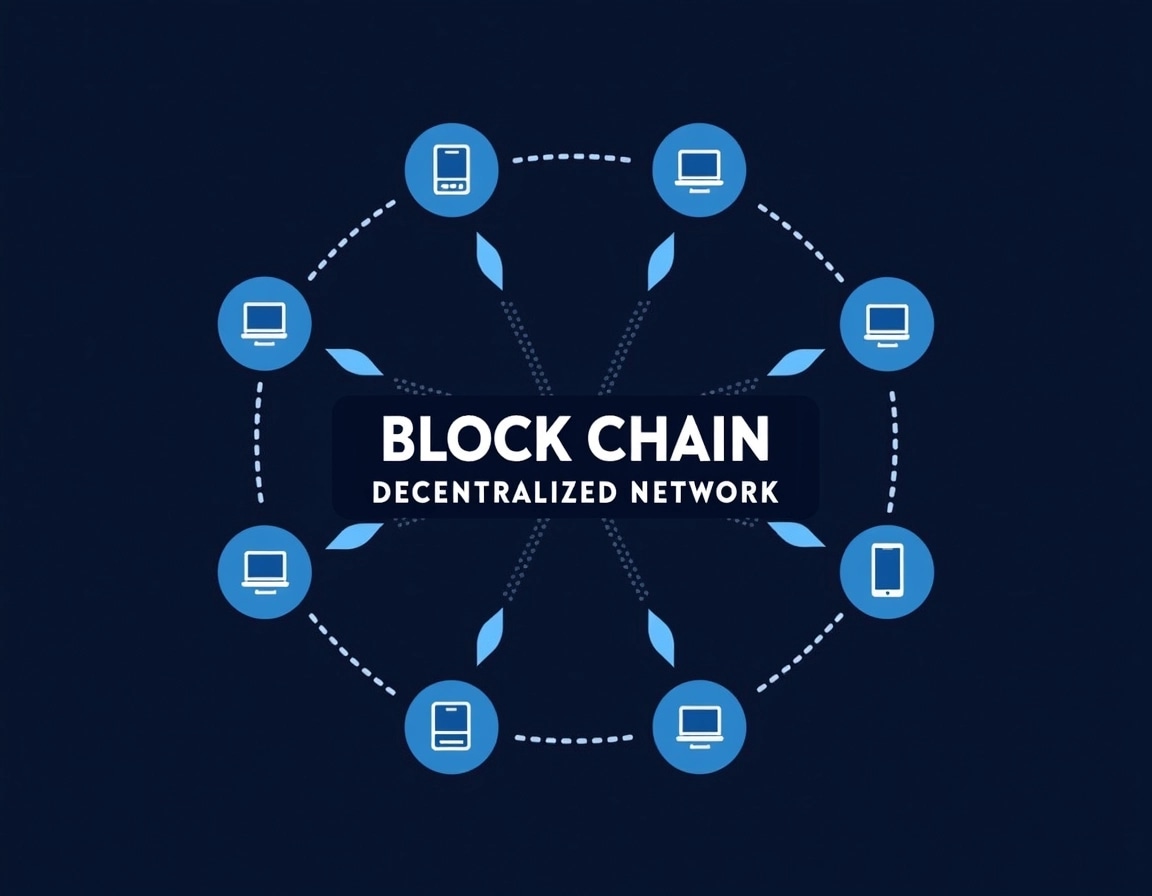
At its core, blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger. But what does that mean, and why should we care?
Let’s start with the basics. A ledger is a record-keeping system. Think of it like a notebook where transactions are written down, keeping track of who owns what. In the traditional world, ledgers are often maintained by a central authority, like a bank or government. This means someone (or some entity) is in charge of verifying and controlling the information.
Blockchain changes that by being decentralized. This means no single person, organization, or authority controls the blockchain. Instead, it’s managed by a network of computers (often called nodes), all of which work together to verify and update the ledger. This decentralized nature makes it more secure, transparent, and resistant to fraud or manipulation.
How Does Blockchain Work?
Imagine a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions. Here’s how the process works in a simplified way:
- Transaction Initiation: Someone wants to make a transaction—say, buying a product or transferring cryptocurrency.
- Verification: This transaction is sent to the blockchain network, where a group of computers (called miners or validators) work to verify it. They check the transaction’s authenticity and ensure that the person initiating it has enough funds (if it’s a payment) or the necessary credentials.
- Block Creation: Once verified, the transaction is grouped together with others into a “block.” This block also contains a cryptographic hash, which is a unique identifier for the block.
- Adding to the Chain: Once the block is complete, it’s added to the existing blockchain. Because each block contains a reference to the previous block, it’s almost impossible to alter any information in a block without changing all subsequent blocks—something that requires massive amounts of computing power.
- Completion: Once the block is added, the transaction is considered complete, and the updated information is accessible to everyone on the network.
Why is Blockchain So Special?
So, why is blockchain causing such a buzz? Here are a few reasons why this technology is gaining so much attention:
1. Decentralization and Trust
One of the biggest advantages of blockchain is its decentralized nature. Since there’s no central authority controlling the system, it’s much harder for any one entity to tamper with the data or manipulate the system. This creates a trustless environment, meaning people can trust the system itself rather than relying on a third party.
2. Transparency
With blockchain, all transactions are recorded on the ledger and visible to everyone in the network. Once data is added to the blockchain, it’s nearly impossible to change or delete. This makes the system transparent, as anyone can verify the transactions and ensure that everything is legitimate.
3. Security
Blockchain uses cryptography to secure the data, making it incredibly difficult for hackers to alter the information. Each block in the chain is linked to the previous one, and changing the data in any block would require changing all the subsequent blocks. This makes blockchain very resistant to fraud and tampering.
4. Faster Transactions
Traditional banking systems can take a few days to process cross-border payments or complex transactions. Blockchain, however, allows for near-instantaneous transactions, even across different countries and currencies. This is especially true with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, which can be transferred 24/7 without needing a bank intermediary.
Real-World Uses of Blockchain
Blockchain is much more than just the backbone of cryptocurrency. While it’s most famous for powering Bitcoin, this technology has a wide range of applications across various industries.
1. Cryptocurrency
The most well-known use of blockchain is cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others. Blockchain serves as the secure, decentralized ledger that records all transactions made with digital currencies. Instead of relying on a central authority like a bank, cryptocurrencies use blockchain to enable peer-to-peer transactions.
2. Supply Chain Management
Blockchain is being used to track the journey of products from the manufacturer to the consumer. For example, in the food industry, blockchain can help track the origin of food products, ensuring that they’re ethically sourced and safe to consume. It can also help prevent fraud in the supply chain by making it easier to trace the authenticity of goods.

3. Healthcare
Blockchain has the potential to improve the way patient data is stored and shared. With a secure, decentralized blockchain system, medical records can be easily accessed and updated by authorized healthcare providers without the risk of hacking or data breaches. Blockchain could also be used for managing the supply of medical drugs, ensuring that only legitimate products reach patients.
4. Voting Systems
Blockchain could revolutionize how we vote in elections. By using blockchain to record votes, we could ensure that the election process is secure, transparent, and tamper-proof. Voters could cast their ballots online, knowing that their votes are recorded accurately and cannot be altered or erased.
5. Digital Identity Verification
Blockchain can also be used for digital identity management. Instead of relying on centralized authorities to verify identities, blockchain could allow individuals to store their personal information securely and share it only when necessary. This could help prevent identity theft and reduce the risk of fraud.
Challenges and Considerations
While blockchain offers many exciting possibilities, it’s not without its challenges. Scalability is one major issue, as blockchain networks can become slow and inefficient as they grow. The energy consumption of blockchain mining (especially in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin) is also a concern, as it requires a significant amount of computational power. Additionally, regulation is still evolving, and there’s a need for clearer laws and frameworks to ensure that blockchain is used responsibly.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain is more than just a buzzword—it’s a transformative technology that has the potential to change how we interact with the digital world. From enhancing transparency and security to enabling faster transactions and decentralized systems, blockchain offers exciting possibilities across industries. While it’s still early in the adoption process, by understanding its core principles and real-world applications, you’re already ahead of the curve.
So, whether you’re interested in cryptocurrency or just curious about this tech revolution, blockchain is definitely something to keep an eye on. It’s not just the future of finance—it’s the future of decentralized, transparent, and secure systems.